Pemetrexed and platinum with or without pembrolizumab for tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-resistant, EGFR-mutant, metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: Phase 3 KEYNOTE-789 study.
Published 06/06/23
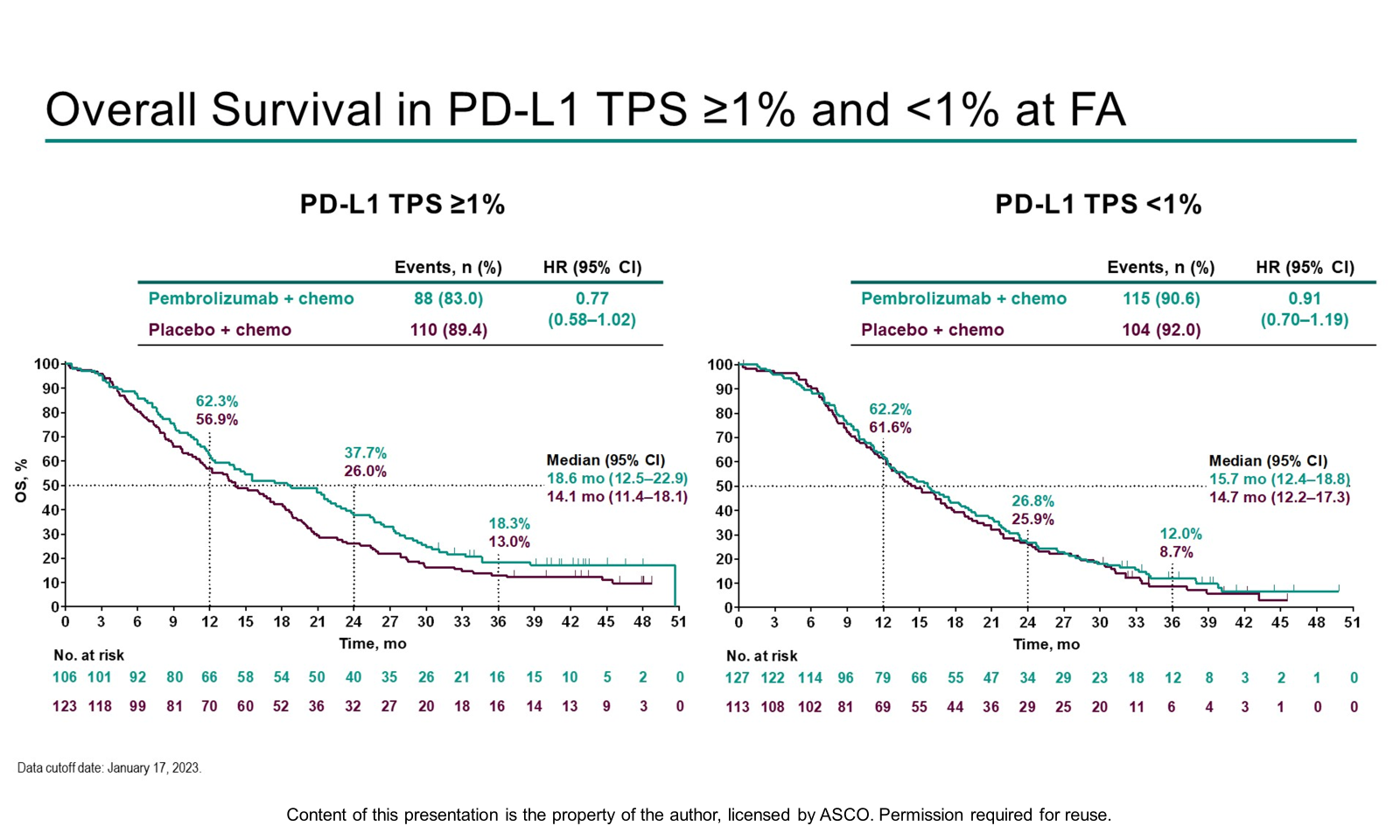
EGFR TKIs are standard 1L therapy for individuals with mNSCLC and sensitizing EGFR mutations, however most patients experience disease progression. TKI-resistant EGFR mutant mNSCLC is associated with poorer survival benefit from anti-PD-(L)1 treatments compared with EGFR wildtype mNSCLC. Data presented today addressed whether adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy provided benefit in survival compared with chemotherapy alone. OS and PFS were improved with pembrolizumab + chemotherapy but did not reach the threshold for statistical significance. PD-L1 TPS ≥1% demonstrated greater benefit compared with TPS <1%, which supports the importance of identifying biomarkers to select patients with EGFR mutant NSCLC who may derive the most benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors.
TROPION-Lung02: Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) plus pembrolizumab (pembro) with or without platinum chemotherapy (Pt-CT) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (aNSCLC).
Published 06/06/23
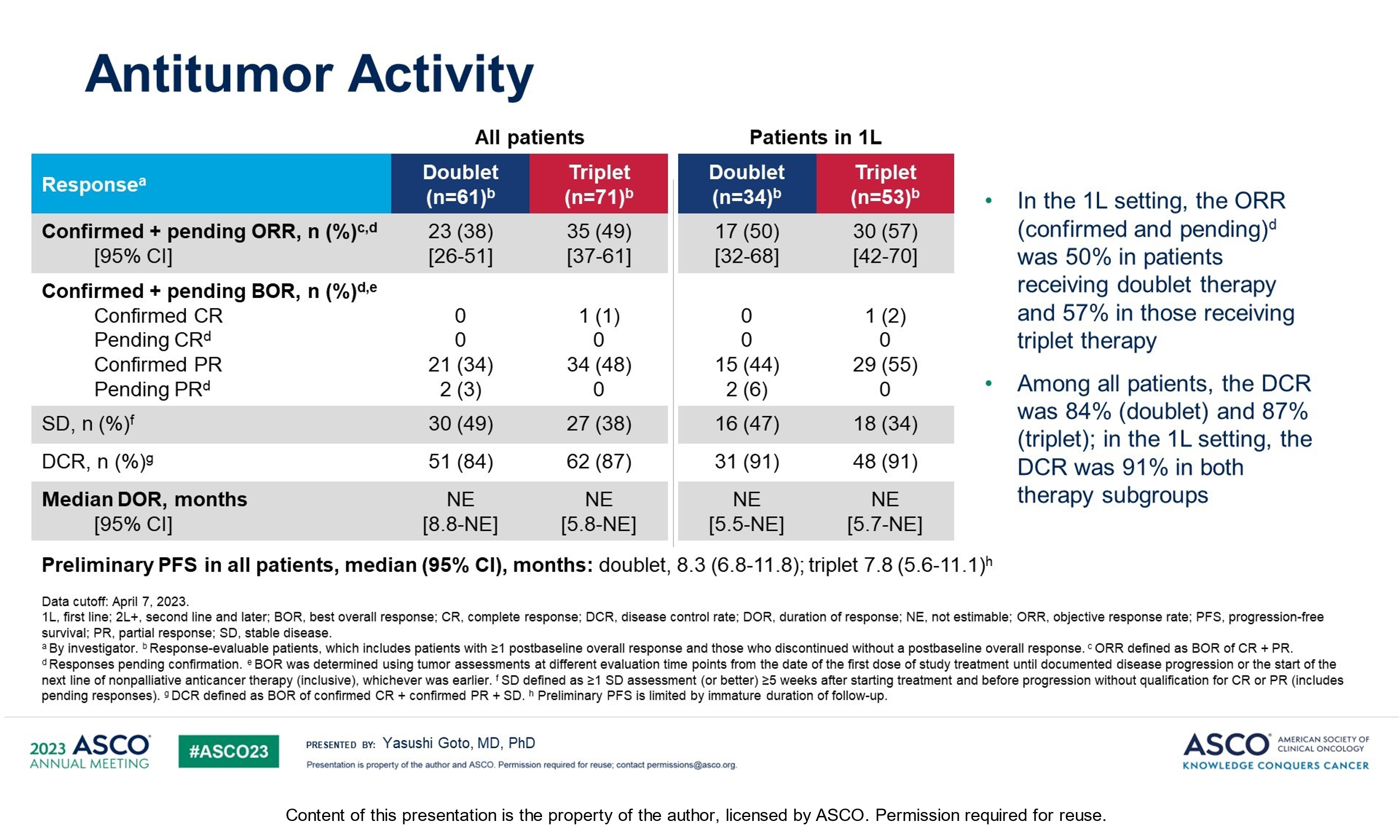
Datopotamab deruxtecan, a TROP2-directed ADC, is being investigated in 1L NSCLC in combination with pembrolizumab. Data from the TROPION-Lung02 trial investigating Dato-Dxd plus pembrolizumab with or without platinum chemotherapy demonstrated encouraging response rates in 1L independent of PD-L1 expression. However, as was highlighted during the discussion session some questions remain, including efficacy versus standard of care, the impact of treatment on patient’s QoL given the reported ocular toxicities, stomatitis, and ILD/pneumonitis, and whether a biomarker strategy may be helpful in identifying patients most likely to respond.
Exploring the role of liso-cel in R/R CLL/SLL: results from TRANSCEND CLL 004
Published 06/06/23
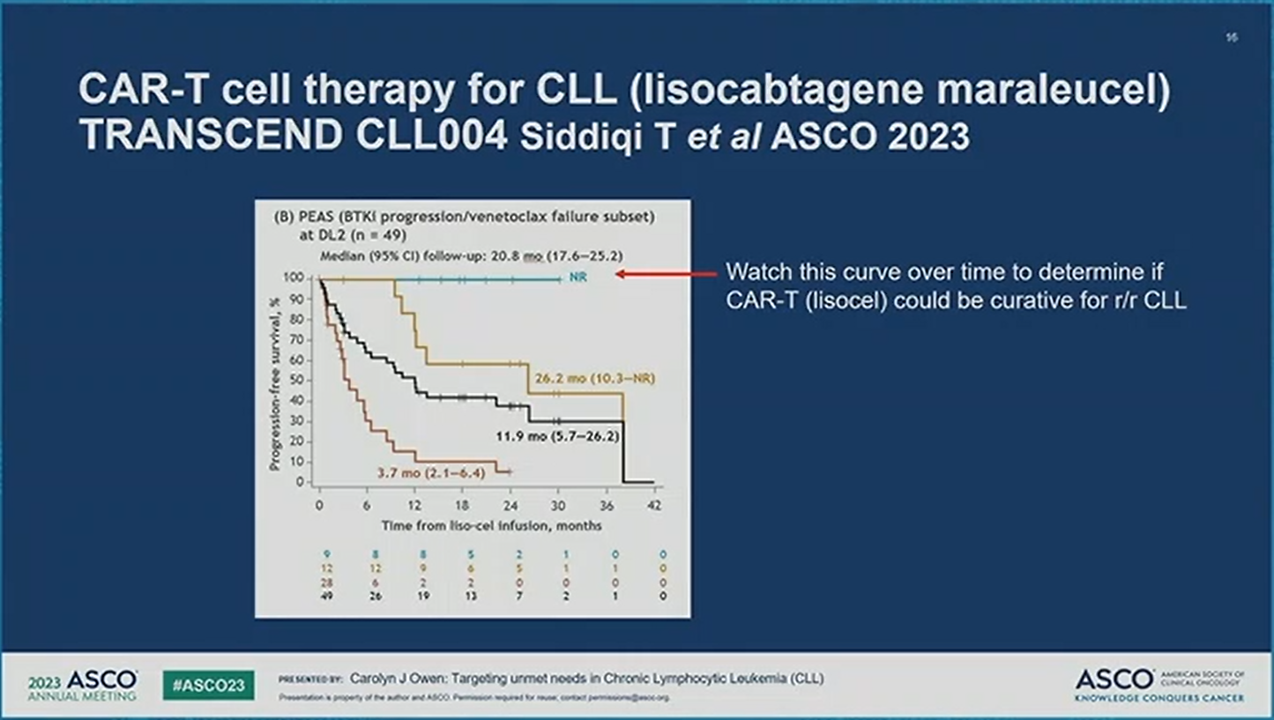
Today's presentation of the primary analysis for liso-cel monotherapy in the TRANSCEND CLL 004 trial showed a statistically significant complete response/remission rate in the double refractory patient population subset of R/R CLL/SLL. ORR was not significant, but uMRD rates were high and occurred early. Efficacy was fairly similar in the full efficacy-evaluable patient subset and the trial had a well-defined double-refractory patient subset. These results suggest that liso-cel can be a potential future therapy for this highly refractory patient population.
Trastuzumab deruxtecan for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and other difficult-to-treat solid tumors sparks conversation at ASCO once again
Published 06/05/23
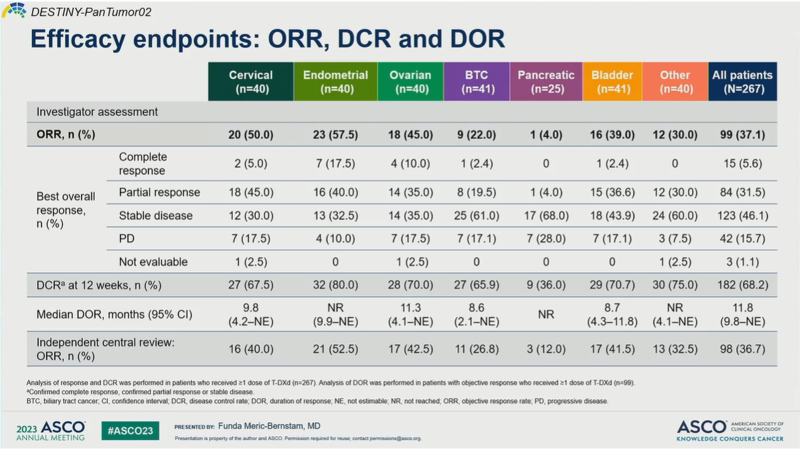
A pooled DESTINY-Breast age-specific analysis of T-DXd demonstrated comparable efficacy and “acceptable” safety of the ADC in those younger vs older than 65 years of age. It has yet to be seen if these outcomes are also replicated in the clinic, as the rates of ILD, the known Achilles heel of T-DXd, do seem to rise as age increases. That said, these data build on the growing pool of evidence supporting efficacy and safety of T-DXd across solid tumor types and come on the heels of a late-breaking presentation of DESTINY-Pantumor02 this morning that has raised the question of whether T-DXd can achieve a tumor-agnostic HER2-targeted label.
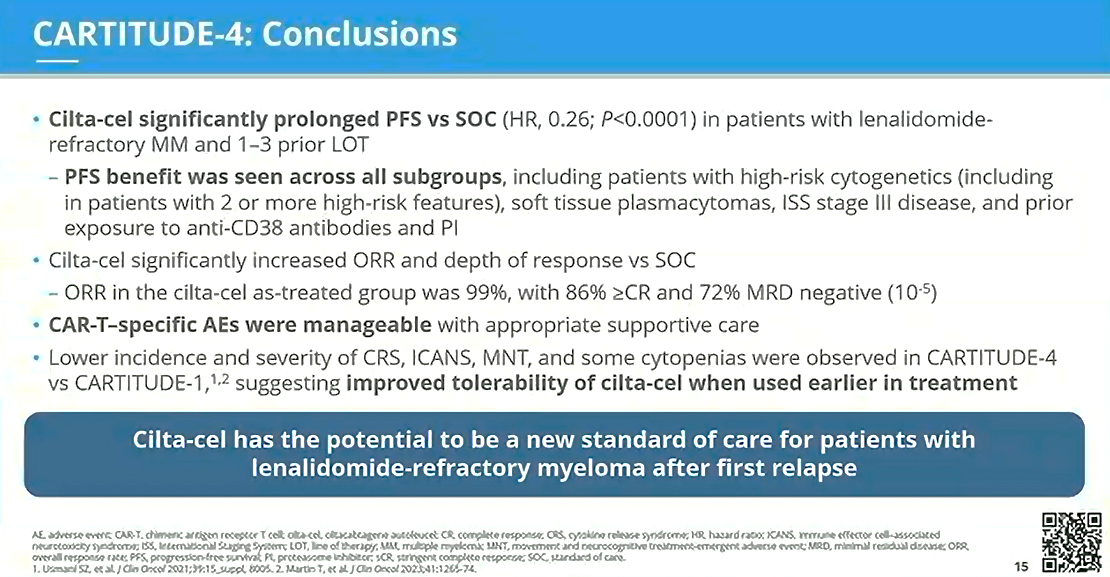
CARTITUDE-4: New potential SOC for patients with lenalidomide-refractory myeloma after first relapse
Published 06/05/23
With a median follow-up of 15.9 months, the CARTITUDE-4 trial met its primary study endpoint of superior PFS (ITT population) vs the SOC (physician’s choice of PVd or DPd). The data, presented by Dr Dhakal, revealed that administering cilta-cel to patients with lenalidomide-refractory MM at an earlier stage of disease resulted in prolonged PFS vs SOC across various subgroups. Cilta-cel significantly increased ORR and depth of response compared to the SOC. CAR-T–specific AEs were reported to be manageable, and when compared to those reported in CARTITUDE-1, appeared to be both less frequent and less severe. The results from CARTITUDE-4 suggest that earlier utilization of cilta-cel in 2L+ RRMM has the potential to be a new SOC for patients with lenalidomide-refractory myeloma after first relapse.
Osimertinib continues to play an important role in early-stage EGFRm NSCLC: OS results from the ADAURA trial
Published 06/04/23
The OS results for the ADAURA trial were presented today in the ASCO plenary session, demonstrating statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefit in OS with adjuvant osimertinib compared to placebo in resected EGFR-mutated stage IB-IIIA NSCLC. The OS hazard ratio of 0.49 signified a 51% reduction in the risk of death with osimertinib. There was an early OS curve separation, sustained beyond 5 years. Osimertinib's safety was consistent with previous reports. These practice-changing data reinforce the established role of osimertinib in this patient population.
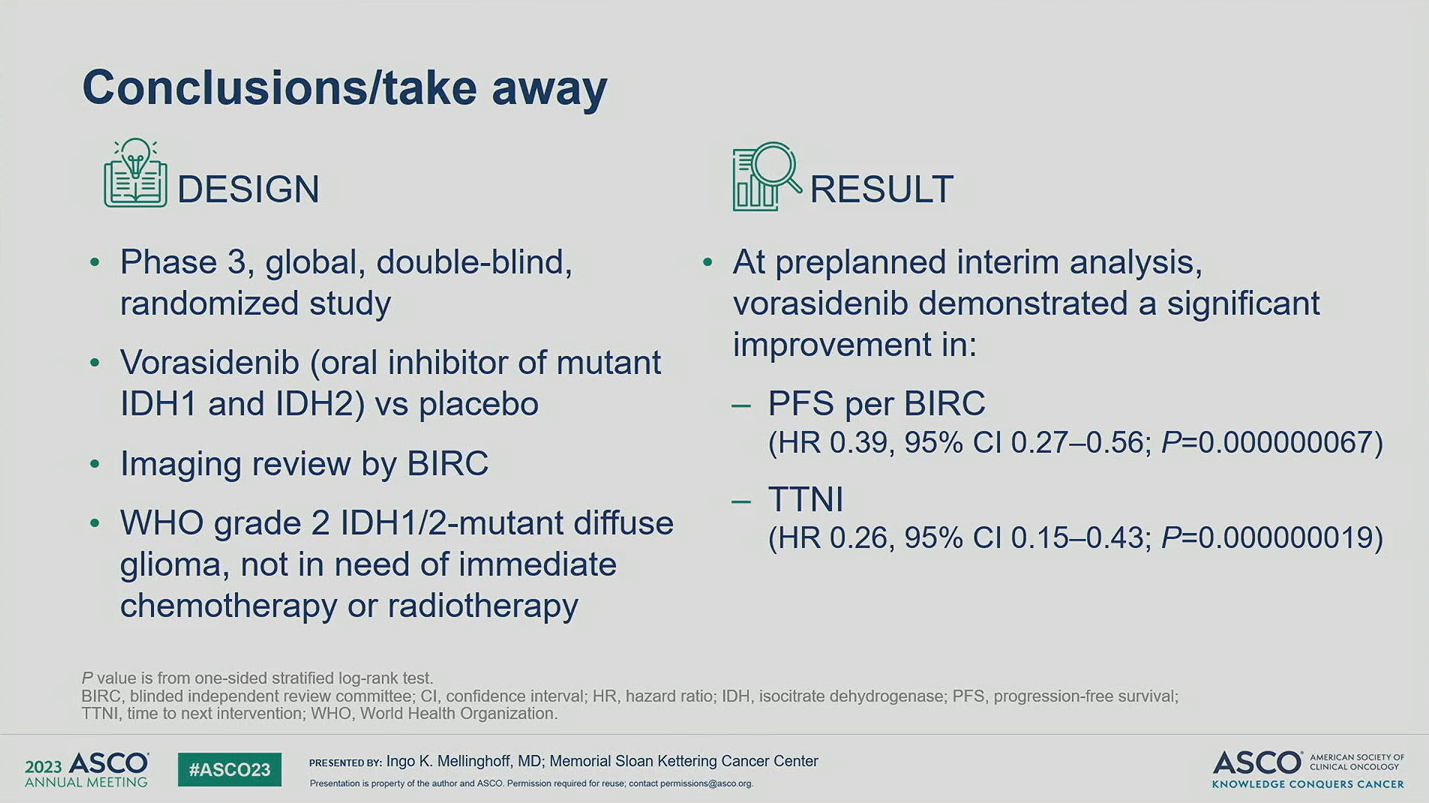
INDIGO: A global, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 study of vorasidenib versus placebo in patients with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1/2 mutation
Published 06/04/23
IDH1/2-mutant grade 2 diffuse gliomas are slow growing but associated with poor prognosis and have no available curative therapy. Remarkable data were presented at ASCO 2023 from an interim analysis of INDIGO, demonstrating vorasidenib’s potential to delay use of toxic chemotherapy and radiation for years in this disease, which will be a major shift in the treatment paradigm. These results also demonstrate that mutant IDH1/2 is a promising target, with future prospects of combination therapy and expansion of indication.
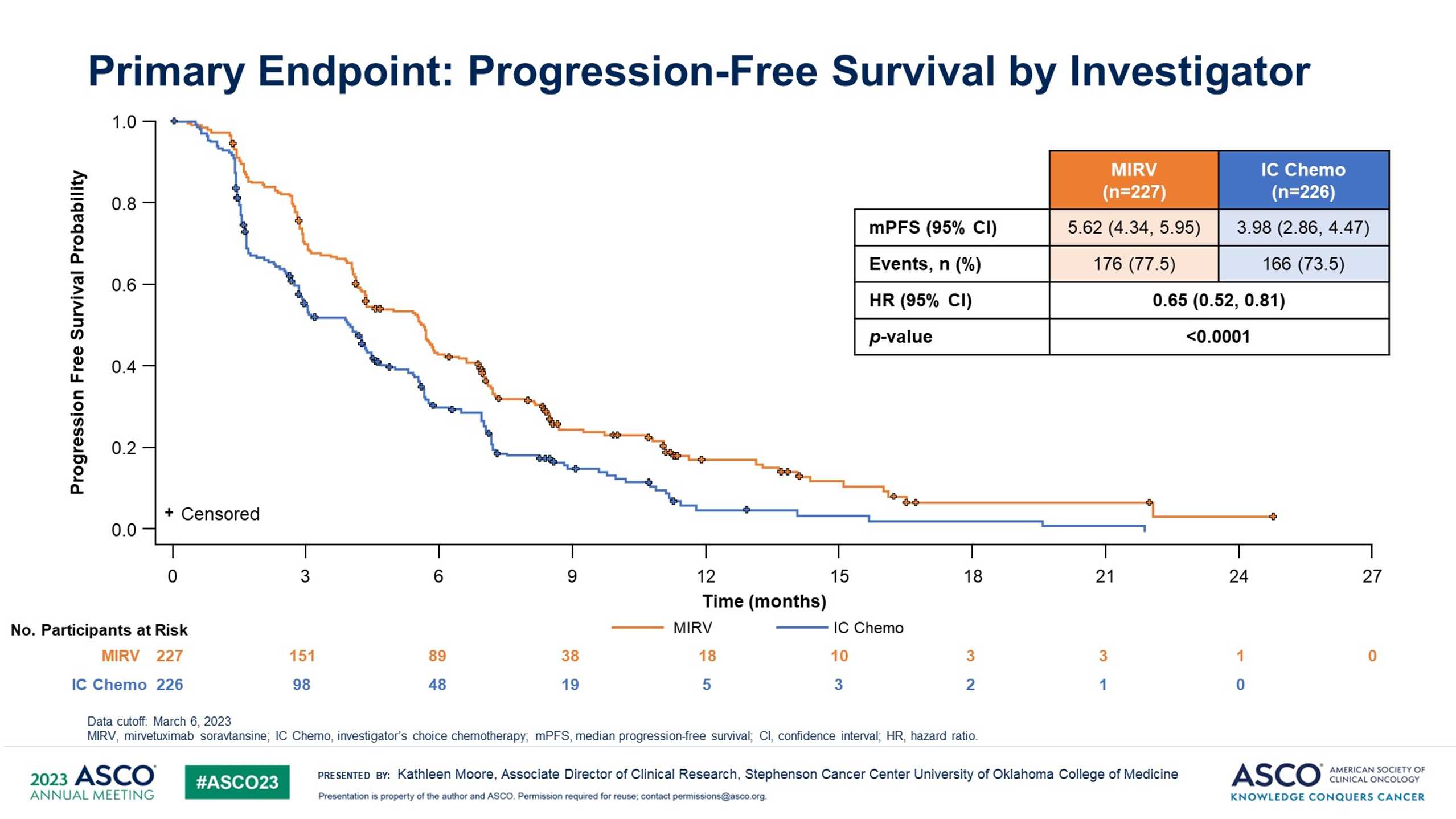
Antibody-drug conjugates evolving the treatment landscape in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer (PROC): results from the MIRASOL trial
Published 06/04/23
The results for the MIRASOL confirmatory trial presented today demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement with mirvetuximab in PFS, ORR, and OS (with OS showing a similar magnitude as PFS), when compared to chemo in folate receptor (FR) α-positive PROC. Mirvetuximab's safety profile continues to be well-characterized, with no new safety signals. These data appear to be practice-changing, suggesting that FRα is an important biomarker to test for and that mirvetuximab could be a standard of care in FRα-positive PROC.
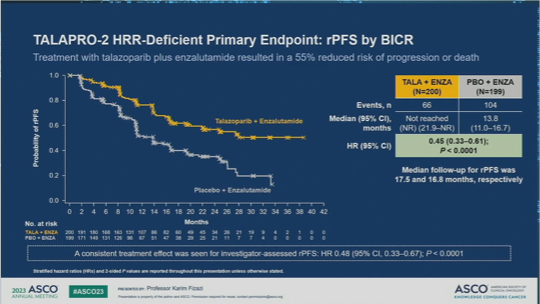
Talazoparib + enzalutamide reinforces the role of PARP and androgen receptor inhibitors in 1L mCRPC harboring homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene alterations
Published 06/04/23
Following clinical benefit in all comers (cohort 1), the combination of talazoparib + enza vs enza + placebo continued to demonstrate positive results in the HRR deficient cohort 2. A significant rPFS clinical benefit with a strong effect in patients with BRCA1/2 mutations was observed with talazoparib + enza. Future questions remain regarding the role of upfront or sequential role of PARP inhibitors in mCRPC.
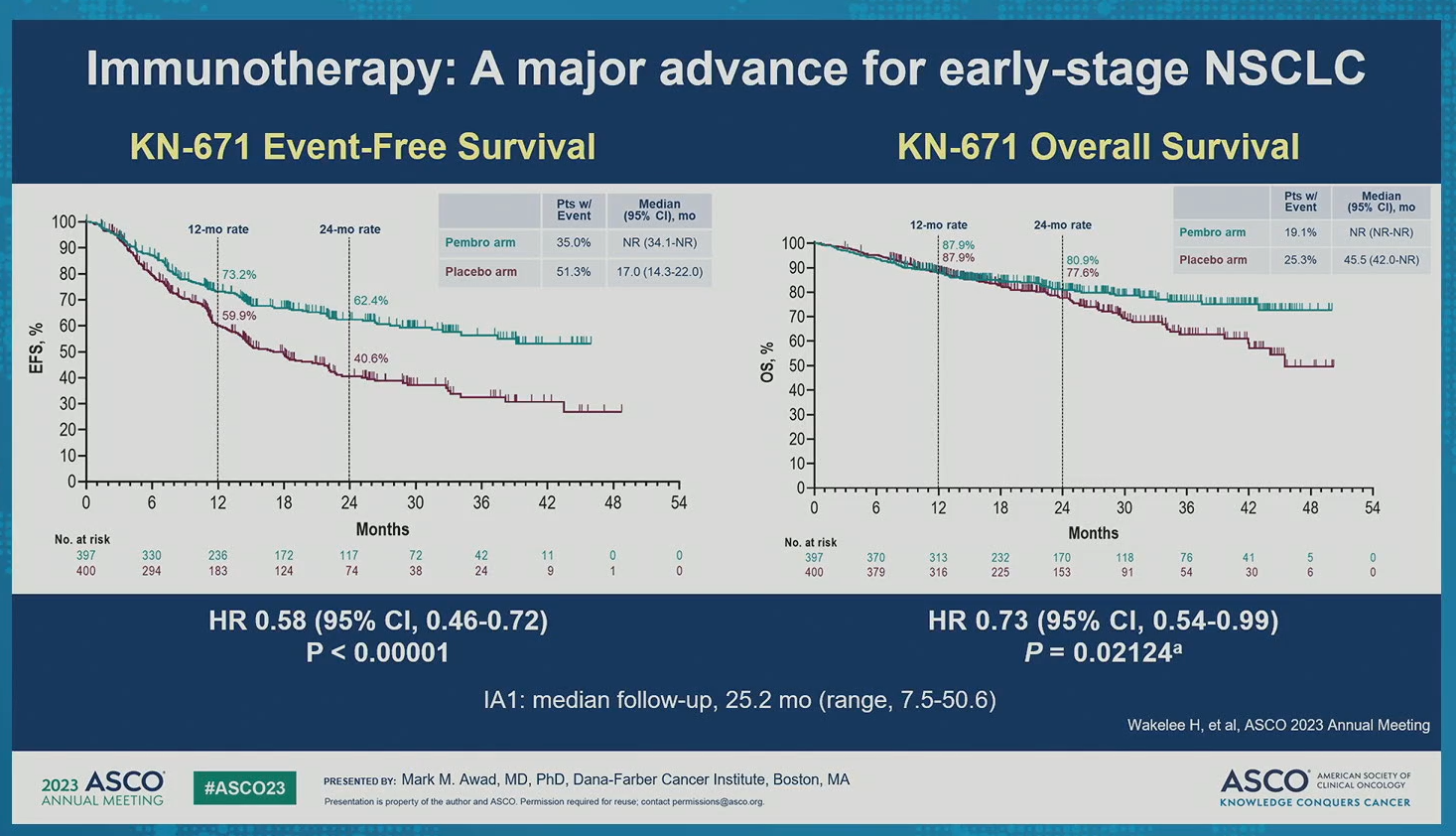
Advances of immunotherapy in early-stage NSCLC: Role of perioperative PD-(L)1 inhibitors
Published 06/03/23
The KEYNOTE-671 trial results presented today demonstrated statistically significant improvement in efficacy (EFS and pCR) for neoadjuvant pembrolizumab + chemo followed by surgery and adjuvant pembrolizumab compared to neoadjuvant chemo and surgery alone. In combination with data from previous perioperative trials, data from KN-671 represent a significant advance for early-stage lung cancer treatment. Moving forward, it will be important to evaluate the contribution of adjuvant vs neoadjuvant treatment.
LBA1013: TORCHLIGHT: A randomized, double-blind, phase III trial of toripalimab versus placebo, in combination with nab-paclitaxel(nab-P) for patients with metastatic or recurrent triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
Published 06/03/23
Metastatic TNBC has a poor prognosis. Although new therapies have shown promise, immune checkpoint inhibitors have had varying success in mTNBC and are currently approved in the CPS ≥ 10% population. TORCHLIGHT, the phase III trial of toripalimab + nab-paclitaxel in patients with mTNBC showed a significant improvement in PFS in the CPS ≥ 1%, with a trend toward improved OS. These results highlight that toripalimab may become an exciting new treatment option for patients with mTNBC.
New kids on the block: Investigation of multiple therapies in ovarian cancer
Published 06/03/23
The gynecologic cancers session today highlighted trials investigating different treatments for ovarian cancer (OC) with positive and negative results. The DUO-O and STRO-002-GM1 trials demonstrated encouraging data for durvalumab + chemo + bevacizumab + olaparib and luveltamab tazevibulin, respectively. Although the OVAL Study trial showed negative results for ofranergene obadenovec, there is much to learn (eg, better identify which patients benefit from which treatments), especially for platinum-resistant OC, which continues to be an area of high unmet need.
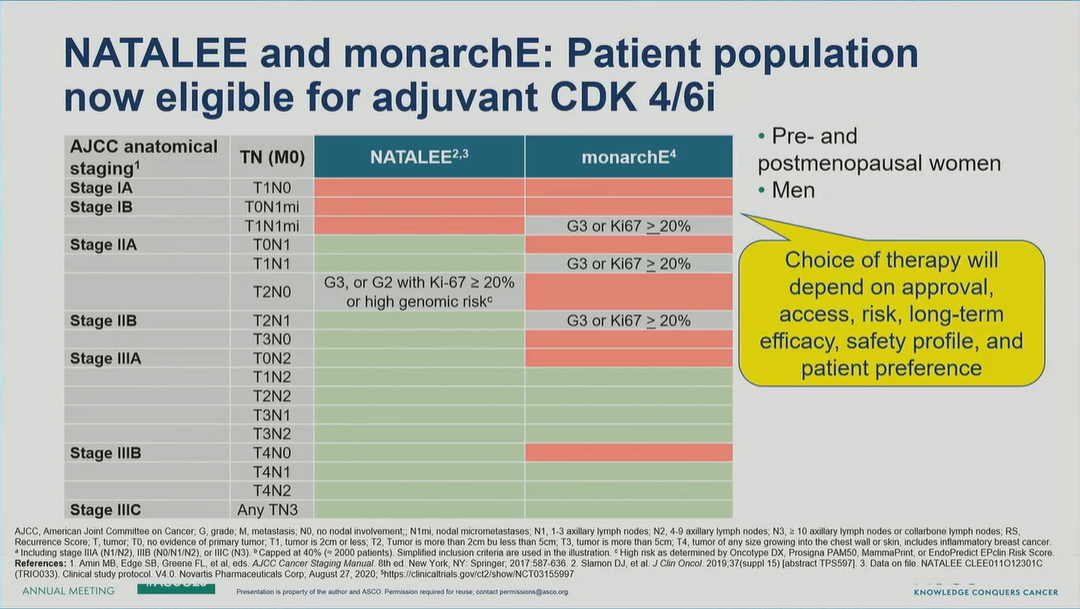
A Tale of Two CDK4/6is: Reducing Risk of Recurrence in HR+/HER2- Early Breast Cancer
Published 06/02/23
Today’s breast cancer oral session showcased the benefits of CDK4/6i as add-on to adjuvant ET in HR+/HER2- early breast cancer, reducing risk of disease recurrence across menopausal status (abemaciclib in monarchE subanalysis by age) and in a population that included node-negative disease (ribociclib in NATALEE interim analysis). These practice-changing data support use of CDK4/6i earlier in the HR+/HER2- treatment plan; longer-term follow-up will further characterize the appropriate patient.
Charging forward in Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Published 06/02/23
Extremely exciting to see two positive Phase 3 trials in LR MDS read out today—a disease that has seen very limited advancements compared with AML. Data from COMMANDS appear paradigm-changing and data from IMerge will bring more treatment options to patients with LR MDS. Questions remain, especially regarding treatment choices based on the presence/absence of ring sideroblasts, but one thing is clear: proactive treatment-planning and sequencing will be key.
Welcome to ASCO 2023!!
Published 06/02/23
We arrived early this morning and can’t wait to take in all of the latest data, discussions, perspectives, and ultimately implications on the way cancer patients are treated across tumor types.